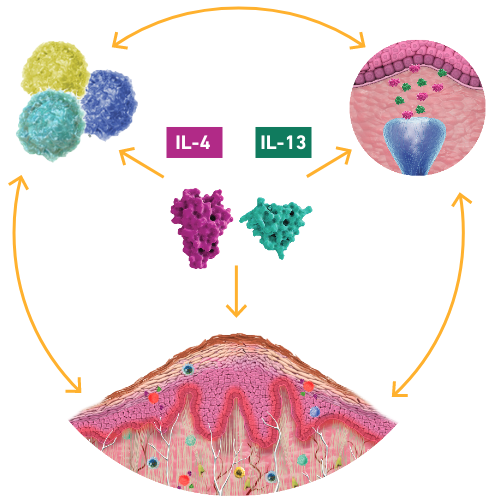
In PN, targeting IL-4 receptor alpha specifically inhibits both IL-4 and IL-13 signaling to help:
REDUCE TYPE 2 INFLAMMATION1,3
REDUCE ITCH1-3
- Helps break itch-scratch cycle
- May reduce neuronal sensitization
ACHIEVE NODULE CLEARANCE1,4-6
- Helps reduce skin fibrosis
The mechanism of dupilumab action has not been definitively established.
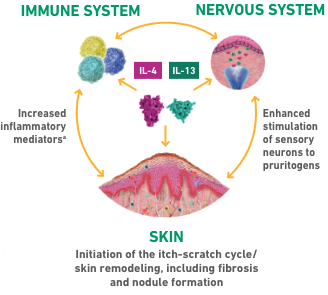
IL-4Rα plays a pivotal role in type 2 inflammation in PN, mediating signaling of IL-4 THROUGH
THE TYPE I RECEPTOR, or IL-4 and/or IL-13 THROUGH the TYPE II RECEPTOR, respectively4-11
Increased IL-4 and IL-13 signaling leads to the itch-scratch cycle and the formation of nodules
The distinct and overlapping roles of IL-4 and IL-134-11
aIncluding Th2, Th17, and Th22 cells, eosinophils, and basophils.8,9
The unique role of IL-4 in type 2 inflammation
IL-4 is an orchestrator of Th2
response, creating a feedback loop that
leads to increased secretion of IL-4,
IL-13, and IL-3112,b,c
bType 2 cytokines (such as IL-4, IL-13, and IL-31) may
also be produced by other immune cells, such as
ILC2.13,14
cIL-4 acts on both type I and type II receptors to
mediate type 2 inflammation.2
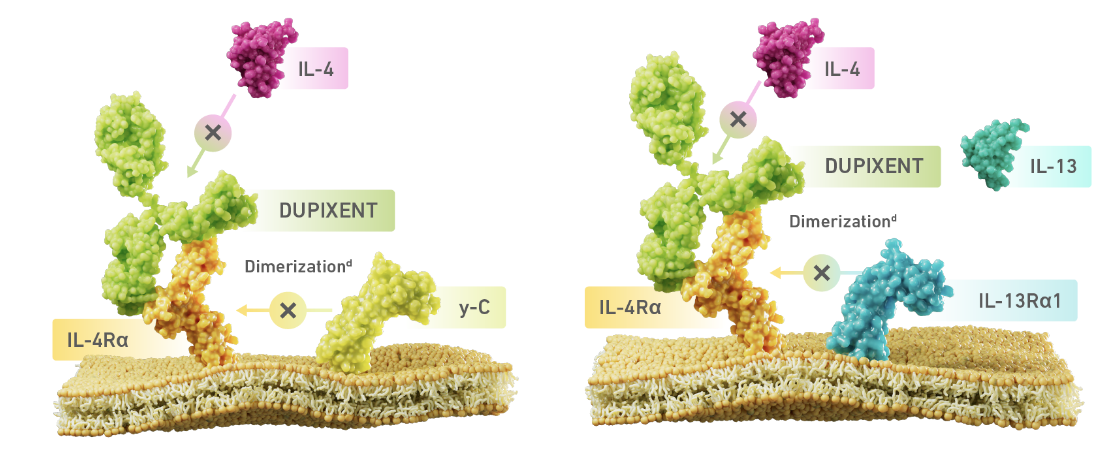
DUPIXENT is the only dual inhibitor of IL-4 and IL-13 signaling1,2
DUPIXENT binds to IL-4 receptor alpha, inhibiting IL-4 and IL-13 induced inflammatory
responses1,2
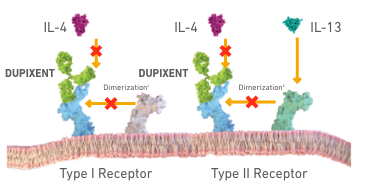
dDimerization is when 2 protein subunits combine to form a larger complex. IL-4 signaling through type I receptor requires dimerization of the Il-4Rα with the gamma chain. IL-4 or Il-13 signaling through type II receptor requires dimerization of IL-4Rα with Il-13Rα1.
IL-4 SIGNALING
(TYPE I RECEPTOR)
IL-4/IL-13 SIGNALING
(TYPE II RECEPTOR)
The mechanism of dupilumab action has not been definitively established.
PN, prurigo nodularis.
IDENTIFY DUPIXENT PATIENTS
Consider whether your patient with prurigo nodularis may be a candidate for DUPIXENT. Take a look at real DUPIXENT stories.