Open Up a World
Where Dual Inhibition
Targets Multiple
Sources
of Disease Heterogeneity
Make DUPIXENT your
first‑choice biologic for your
appropriate asthma patients
How DUPIXENT
Works
DUPIXENT is the only dual
inhibitor of IL‑4 and IL‑13
signaling, two of the key
drivers of local and systemic
type 2 inflammation
in asthma1-4,a
a The mechanism of dupilumab action
has not been definitively established.1
What are two of the key sources of local type 2 inflammation in asthma?
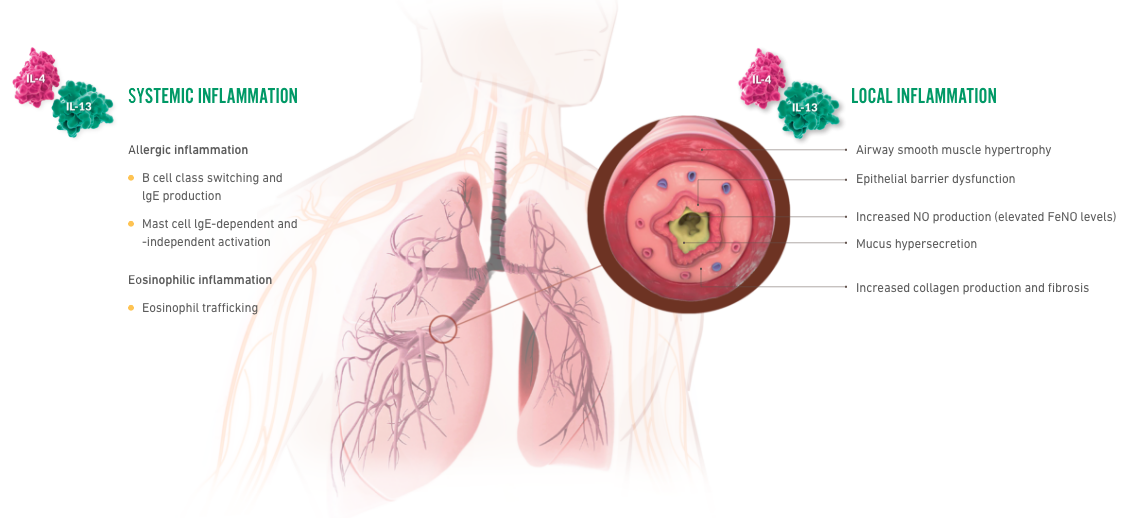
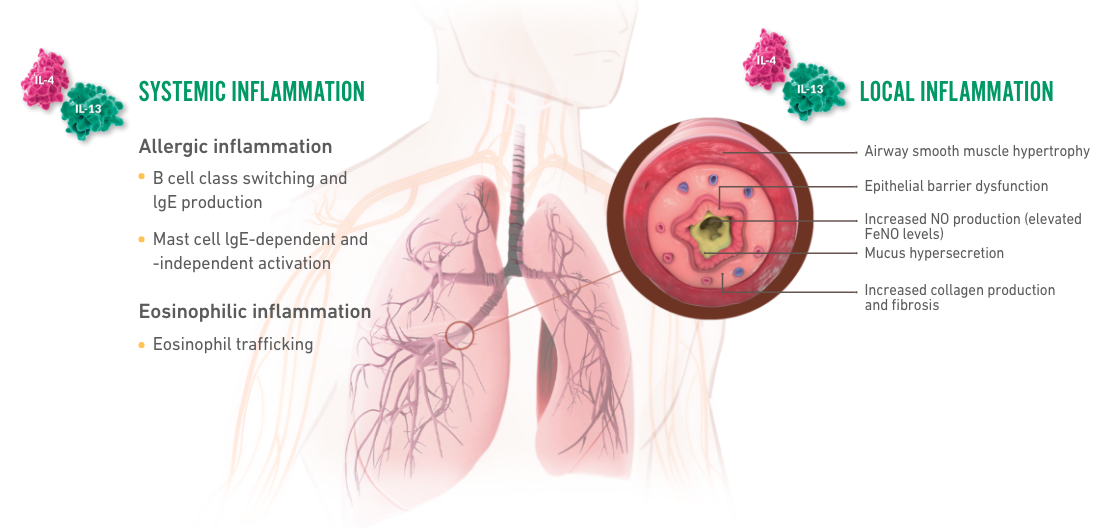
Patients who suffer with asthma may be sensitive to potential triggers that can initiate an asthma exacerbation. Let’s take a deep look inside the lower respiratory epithelium to see what happens during an asthma exacerbation. When patients with asthma encounter potential triggers, this can lead to epithelial inflammation and alarmin activation. This trigger can also lead to signaling of Th2 cells and ILC2s which release cytokines such as IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13. Let’s look inside the epithelium to focus on IL-13 and its role in type 2 inflammation. IL-13 is a key source of local type 2 inflammation. When activated, it contributes to epithelial barrier dysfunction, eosinophilic inflammation, mucus overproduction and smooth muscle contraction.
How do eosinophils contribute to systemic type 2 inflammation in asthma?
IL-4 is a key source of systemic type 2 inflammation that causes eosinophil trafficking to the site of inflammation. Eosinophils release eosinophilic cationic protein or ECP, eosinophil peroxidase or EPO, and other chemical mediators that contribute to asthma pathology. IL-4 also causes B cell activation, IGE production, as well as mass cell and basophil activation, and trafficking. IGE binds to receptors on the surface of mast cells and basophils and cross links with antigen. This results in mast cell and basophil degranulation releasing additional cytokines, histamines and leukotrienes.
Did you know that DUPIXENT targets two of the sources of type 2 inflammation?
DUPIXENT is the only dual-inhibitor of IL-4 and IL-13 signaling, two of the key drivers of local and systemic type 2 inflammation. The mechanism of dupilumab action has not been definitively established. There are two types of receptors blocked by DUPIXENT: the type 1 receptor and the type 2 receptor. Type 1 receptors are located within the cell membranes of mast cells, basophils, eosinophils, neutrophils and T cells. Type 2 receptors are located within the cell membranes of epithelial cells, smooth muscle cells and fibroblasts. DUPIXENT binds to the IL-4 receptor blocking IL-4 and IL-13 intracellular signaling. Pharmacodynamics data with DUPIXENT showed a decrease in total IGE and a transient increase in blood eosinophils. DUPIXENT also prevents complexing of IL-13 receptor with the IL-4 receptor complex. Pharmacodynamics data with DUPIXENT showed decreased FeNO levels. In clinical trials, patients with uncontrolled asthma, treated with DUPIXENT experienced up to 35% reduction from baseline at week 96 in blood eosinophils, up to 83% reduction from baseline at week 96 in total IGE, and up to 35% reduction from baseline in FeNo after two weeks. Correlations between pharmacodynamics data and efficacy endpoints have not been established. Results are descriptive.
Make DUPIXENT your first-choice biologic for your appropriate patients with an eosinophilic phenotype or OCS-dependent asthma, driven by type 2 inflammation.
DUPIXENT IS NOT
AN IMMUNOSUPPRESSANT1
How DUPIXENT Works
DUPIXENT is the only dual inhibitor of IL-4 and IL-13 signaling, two of the key drivers of local and systemic type 2 inflammation in asthma1-5,a
aThe mechanism of dupilumab action has not been definitively established.1

What are two of the key sources of local type 2 inflammation in asthma?
Patients who suffer with asthma may be sensitive to potential triggers that can initiate an asthma exacerbation. Let’s take a deep look inside the lower respiratory epithelium to see what happens during an asthma exacerbation. When patients with asthma encounter potential triggers, this can lead to epithelial inflammation and alarmin activation. This trigger can also lead to signaling of Th2 cells and ILC2s which release cytokines such as IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13. Let’s look inside the epithelium to focus on IL-13 and its role in type 2 inflammation. IL-13 is a key source of local type 2 inflammation. When activated, it contributes to epithelial barrier dysfunction, eosinophilic inflammation, mucus overproduction and smooth muscle contraction.
How do eosinophils contribute to systemic type 2 inflammation in asthma?
IL-4 is a key source of systemic type 2 inflammation that causes eosinophil trafficking to the site of inflammation. Eosinophils release eosinophilic cationic protein or ECP, eosinophil peroxidase or EPO, and other chemical mediators that contribute to asthma pathology. IL-4 also causes B cell activation, IGE production, as well as mass cell and basophil activation, and trafficking. IGE binds to receptors on the surface of mast cells and basophils and cross links with antigen. This results in mast cell and basophil degranulation releasing additional cytokines, histamines and leukotrienes.
Did you know that DUPIXENT targets two of the sources of type 2 inflammation?
DUPIXENT is the only dual-inhibitor of IL-4 and IL-13 signaling, two of the key drivers of local and systemic type 2 inflammation. The mechanism of dupilumab action has not been definitively established. There are two types of receptors blocked by DUPIXENT: the type 1 receptor and the type 2 receptor. Type 1 receptors are located within the cell membranes of mast cells, basophils, eosinophils, neutrophils and T cells. Type 2 receptors are located within the cell membranes of epithelial cells, smooth muscle cells and fibroblasts. DUPIXENT binds to the IL-4 receptor blocking IL-4 and IL-13 intracellular signaling. Pharmacodynamics data with DUPIXENT showed a decrease in total IGE and a transient increase in blood eosinophils. DUPIXENT also binds to the IL-13 receptor preventing IL-13 receptor binding with IL-13 as well as complexing of IL-13 receptor with the IL-4 receptor complex. Pharmacodynamics data with DUPIXENT showed decreased FeNO levels. In clinical trials, patients with uncontrolled asthma, treated with DUPIXENT experienced up to 35% reduction from baseline at week 96 in blood eosinophils, up to 83% reduction from baseline at week 96 in total IGE, and up to 35% reduction from baseline in FeNo after two weeks. Correlations between pharmacodynamics data and efficacy endpoints have not been established. Results are descriptive.
Make DUPIXENT your first-choice biologic for your appropriate patients with an eosinophilic phenotype or OCS-dependent asthma, driven by type 2 inflammation.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION & INDICATION
CONTRAINDICATION: DUPIXENT is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to dupilumab or any of its excipients.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Hypersensitivity: Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, serum sickness or serum sickness-like reactions, angioedema, generalized urticaria, rash, erythema nodosum, and erythema multiforme have been reported. If a clinically significant hypersensitivity reaction occurs, institute appropriate therapy and discontinue DUPIXENT.
Eosinophilic Conditions: Patients being treated for asthma may present with serious systemic eosinophilia sometimes presenting with clinical features of eosinophilic pneumonia or vasculitis consistent with eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA), conditions which are often treated with systemic corticosteroid therapy. These events may be associated with the reduction of oral corticosteroid therapy. Healthcare providers should be alert to vasculitic rash, worsening pulmonary symptoms, cardiac complications, and/or neuropathy presenting in their patients with eosinophilia. Cases of eosinophilic pneumonia were reported in adult subjects who participated in the asthma development program and cases of vasculitis consistent with EGPA have been reported with DUPIXENT in adult subjects who participated in the asthma development program as well as in adult subjects with co-morbid asthma in the chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis development program. A causal association between DUPIXENT and these conditions has not been established.
Acute Asthma Symptoms or Deteriorating Disease: Do not use DUPIXENT to treat acute asthma symptoms, acute exacerbations, acute bronchospasm or status asthmaticus. Patients should seek medical advice if their asthma remains uncontrolled or worsens after initiation of DUPIXENT.
Risk Associated with Abrupt Reduction of Corticosteroid Dosage: Do not discontinue systemic, topical, or inhaled corticosteroids abruptly upon initiation of DUPIXENT. Reductions in corticosteroid dose, if appropriate, should be gradual and performed under the direct supervision of a healthcare provider. Reduction in corticosteroid dose may be associated with systemic withdrawal symptoms and/or unmask conditions previously suppressed by systemic corticosteroid therapy.
Arthralgia: Arthralgia has been reported with use of DUPIXENT with some patients reporting gait disturbances or decreased mobility associated with joint symptoms; some cases resulted in hospitalization. Advise patients to report new onset or worsening joint symptoms. If the symptoms persist or worsen, consider rheumatological evaluation and/or discontinuation of DUPIXENT.
Parasitic (Helminth) Infections: It is unknown if DUPIXENT will influence the immune response against helminth infections. Treat patients with pre-existing helminth infections before initiating therapy with DUPIXENT. If patients become infected while receiving treatment with DUPIXENT and do not respond to anti-helminth treatment, discontinue treatment with DUPIXENT until the infection resolves. Helminth infections (5 cases of enterobiasis and 1 case of ascariasis) were reported in pediatric patients 6 to 11 years old in the pediatric asthma development program.
Vaccinations: Consider completing all age-appropriate vaccinations as recommended by current immunization guidelines prior to initiating DUPIXENT. Avoid use of live vaccines during treatment with DUPIXENT.
ADVERSE REACTIONS: The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥1%) in patients with asthma are injection site reactions, oropharyngeal pain, and eosinophilia.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Pregnancy: A pregnancy exposure registry monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to DUPIXENT during pregnancy. To enroll or obtain information call 1‑877‑311‑8972 or go to https://mothertobaby.org/ongoing-study/dupixent/. Available data from case reports and case series with DUPIXENT use in pregnant women have not identified a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Human IgG antibodies are known to cross the placental barrier; therefore, DUPIXENT may be transmitted from the mother to the developing fetus.
- Lactation: There are no data on the presence of DUPIXENT in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Maternal IgG is known to be present in human milk. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for DUPIXENT and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from DUPIXENT or from the underlying maternal condition.
Please see accompanying full Prescribing Information.
INDICATION
DUPIXENT is indicated as an add-on maintenance treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 6 years and older with moderate-to-severe asthma characterized by an eosinophilic phenotype or with oral corticosteroid dependent asthma. Limitation of Use: DUPIXENT is not indicated for the relief of acute bronchospasm or status asthmaticus.
Up to 84% of adult asthma patients present
with type 2 inflammation5,6
IL-4 and IL-13
contribute to multiple
systemic
inflammatory
effects in asthma2-4
IL-4 and IL-13 contribute
to multiple local
inflammatory effects in
the bronchial tubes2-4
GINA guidelines define type 2 inflammation as an immune response identified in part by 1 or more biomarkers7
FeNO, fractional exhaled nitric oxide; GINA, Global Initiative for Asthma; NO, nitric oxide.
Open Up a World Where More Than
One Patient Type Can Be Treated
Discover how DUPIXENT works in various patient types.