DUPIXENT IS THE ONLY
FDA-APPROVED DUAL INHIBITOR
OF IL‑4 AND IL‑13 SIGNALING1,a
See how DUPIXENT works
DUPIXENT INHIBITS IL-4 AND IL-13 SIGNALING, TARGETING EoE AT TWO OF THE KEY SOURCES1-4,a
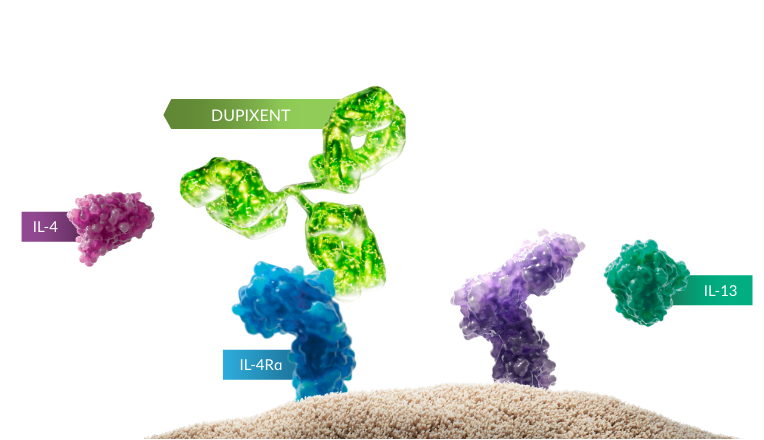
aThe mechanism of dupilumab action has not been definitively established.1
IL-4 AND IL-13 ARE TWO OF THE KEY DRIVERS OF TYPE 2 INFLAMMATION THAT
RESULT IN PATHOLOGICAL CHANGES AND SYMPTOMS OF EoE2-4
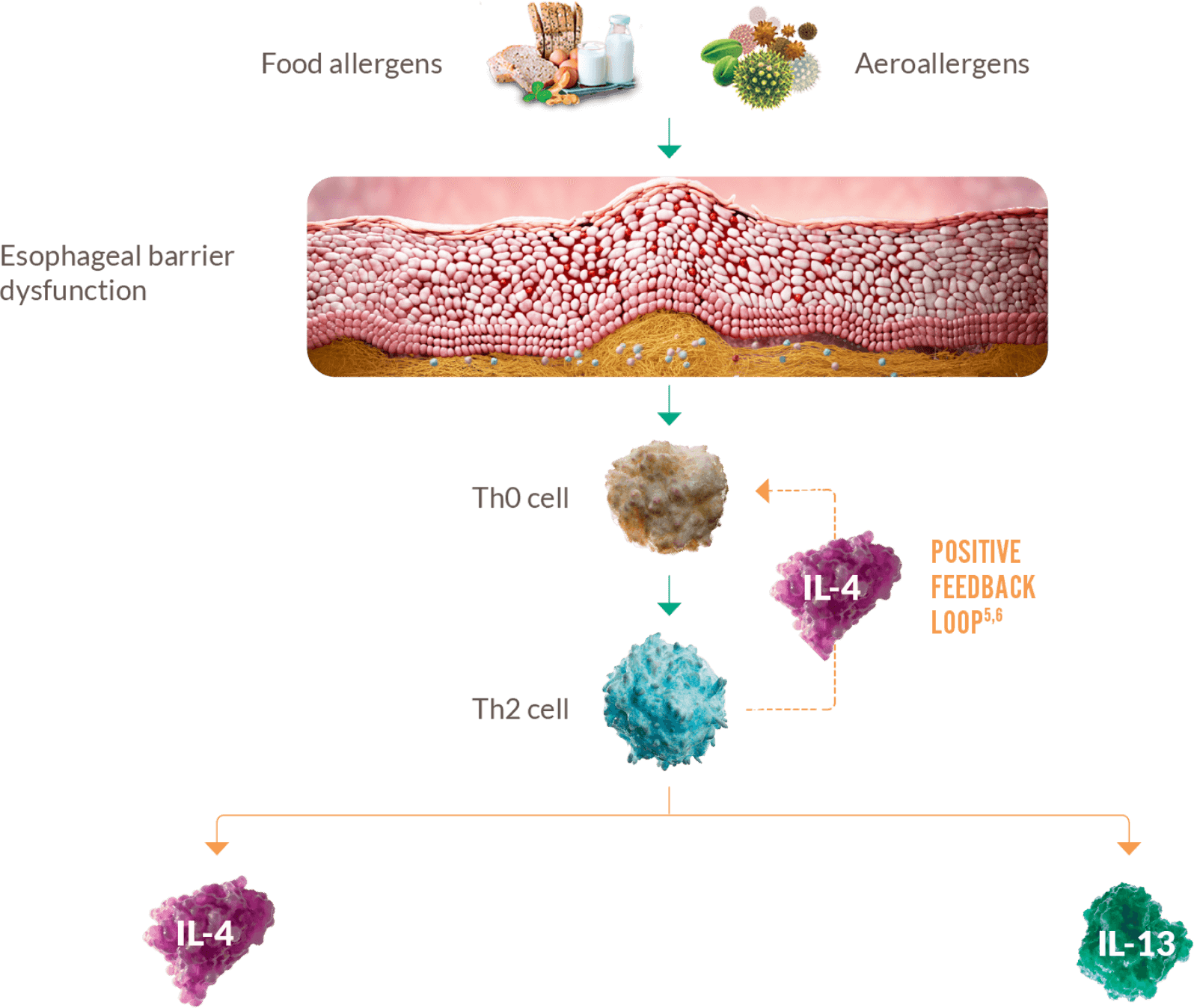
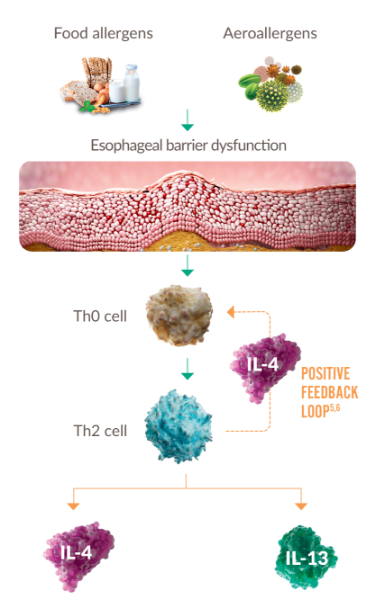
- Amplifies and sustains type 2 inflammation
- IgE antibody production
- Mast cell proliferation and survival
- Epithelial barrier disruption
- Eosinophil activation
- Tissue inflammation
- Fibrosis
- Esophageal remodeling
- Esophageal muscular dysfunction
Adult/adolescent
(≥12 years)
Food
impaction
Dysphagia
Heartburn/
acid reflux
Painful
swallowing
Pediatric
(1-11 years)
Stomach
pain
Food
refusal
Heartburn/
acid reflux
Regurgitation/
vomiting
Only DUPIXENT directly inhibits the signaling of two of the key drivers of type 2 inflammation contributing to EoE.1,2
signaling 1,2
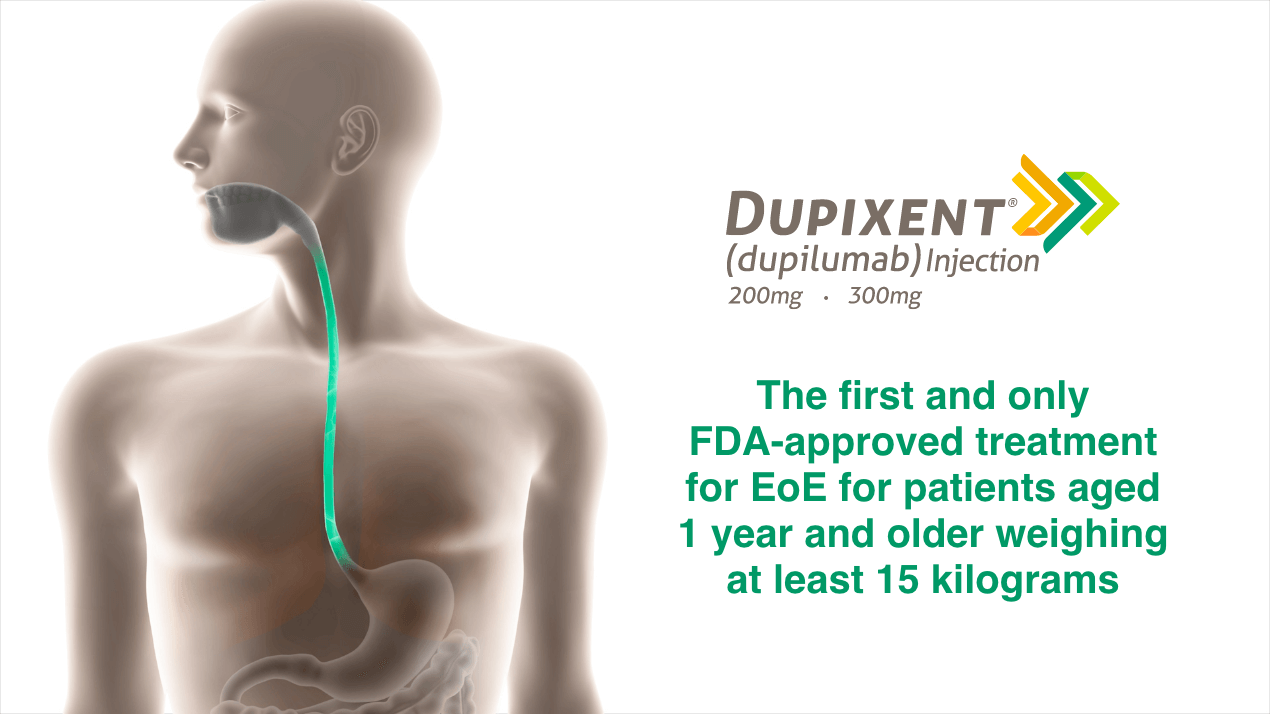
Helps target underlying inflammation in EoE1,2
Clinical outcomes10
Impact on frequency and
severity of symptoms
Histologic outcomes10
Impact on eosinophilic
inflammation
Endoscopic outcomes10
Impact on visible
inflammation and fibrosis
in the esophagus
The mechanism of dupilumab action has not been definitively established.1
Meet Dr. Joshua Wechsler, MD, MSCI
Listen to Dr. Wechsler’s insight for helping pediatric
patients articulate their symptoms.

Dr. Wechsler, MD, MSCI
Typically when I’m talking to a patient for the first time about a new EoE diagnosis, for me, I’m really focused in on the fact that this is chronic disease. They’re most likely going to have it lifelong and that if we don’t really treat this disease, it’s going to lead to narrowing of the esophagus, which means food’s going to get stuck. I think that’s probably more challenging when they’re young and it’s really hard to perceive those. When you experience it, it’s probably even more real.
Discover appropriate EoE patients