Watch the video to see how DUPIXENT works.
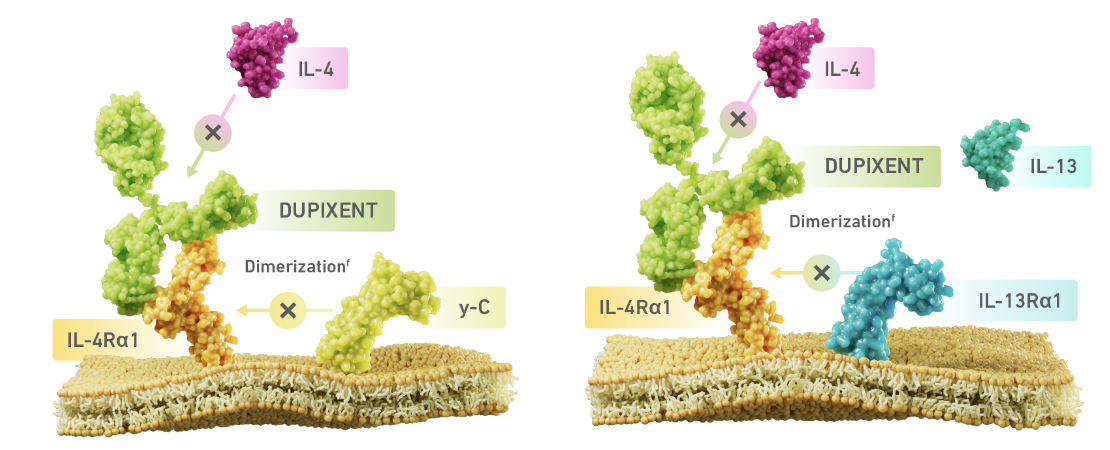
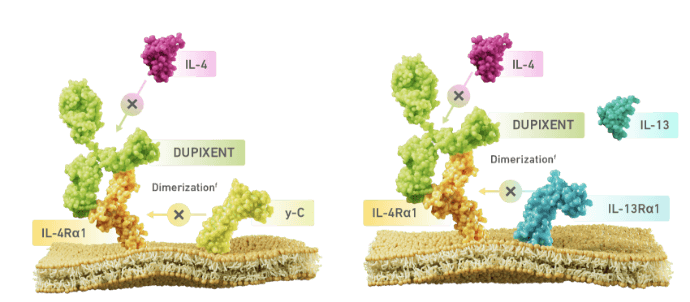
DUPIXENT BINDS TO IL-4Rα, INHIBITING IL-4 AND IL-13 SIGNALING
Dual inhibition of IL-4 and IL-13 signaling helps5:
REDUCE TYPE 2
INFLAMMATION
REDUCE
ITCH
REDUCE
HIVES
The mechanism of dupilumab action
has not been definitively established.
TYPE 2 INFLAMMATION MAY CONTRIBUTE TO DISEASE CHRONICITY IN CSU
Watch the video to see how DUPIXENT works.
Type 2 cytokines, including IL‑4 and IL‑13, may
contribute to
multiple aspects
of mast cell activation and degranulation2‑4,6‑11
Enhance IgE and IgG production
Increase expression of FcεRIa
Enhance neurosensitization to pruritogens
(eg, histamine, other mediators)b
Increase recruitment of type 2 inflammatory cells
(eg, basophils, eosinophils, B cells, and T cells)c
FcεRI, high-affinity IgE receptor.
a This leads to mast cell priming and degranulation. Activated mast cells release IL-4 and IL-13 and contribute to type 2 inflammation in CSU.8
b Itch signals can, in turn, induce further immune activation and release of inflammatory mediators, creating a feedback loop.12,13
c IL-5 may also play a role in skin homing of eosinophils as well as in their maturation and survival.14
d Th2 cells produce IL-4 and IL-13, which enhance B cell production of IgE and IgG antibodies.6,8
e Mast cells can be activated through pathways that are IgE dependent or independent, leading to degranulation and the release of histamine
and other immune mediators.11
Watch the video to see how DUPIXENT works.
DUPIXENT binds to IL-4
receptor alpha, inhibiting IL-4
and IL-13
induced
inflammatory responses
The mechanism of dupilumab action has not been definitively established.
- fDimerization is when 2 protein subunits combine to form a larger complex. IL-4 signaling through type I receptor requires dimerization of the Il-4Rα with the gamma chain. IL-4 or Il-13 signaling through type II receptor requires dimerization of IL-4Rα with Il-13Rα1.
IL-4 SIGNALING
(TYPE I RECEPTOR)
IL-4/IL-13 SIGNALING
(TYPE II RECEPTOR)
TAKE A LOOK AT
PATIENT PROFILES
Consider whether your appropriate CSU patient may be a
candidate for DUPIXENT.